无重复字符的最长子串 给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入: s = "bbbbb" 输出: 1 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "b",所以其长度为 1。
分析: 双指针,l是左边,i是右边,不断变换l,如果遇到相同的元素,则改变l,l变为最后出现相同值得下一个位置。max是存储最大长度。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {new HashMap <>();int l = 0 ;int max = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i<s.length();i++){char ch = s.charAt(i);if (map.containsKey(ch)){1 );1 );return max;
LRU 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 class LRUCache {class TwoLinked {int value;int key;public TwoLinked () {}public TwoLinked (int key,int value) {this .key = key;this .value = value;new HashMap <>();int size;int capacity;public LRUCache (int capacity) {this .size = 0 ;this .capacity = capacity;new TwoLinked ();new TwoLinked ();public int get (int key) {TwoLinked twoLinked = map.get(key);if (twoLinked!=null ){int v = twoLinked.value;return v;else {return -1 ;public void put (int key, int value) {TwoLinked twoLinked1 = map.get(key);if (twoLinked1!=null ){else {if (map.size()==capacity){TwoLinked newLinked = new TwoLinked (key, value);public void deleteLastLinked () {public void removeToHead (TwoLinked linked) {public void deleteLinked (TwoLinked linked) {public void addHeadLinked (TwoLinked linked) {
K个一组翻转链表 给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] , k = 2 [2,1,4,3,5]
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 );ListNode pre = dummy;ListNode end = dummy;while (end!=null ){for (int i = 0 ;i<k && end!=null ;i++){if (end==null ) break ;ListNode start = pre.next;ListNode next = end.next;null ;return dummy.next;public ListNode reverse (ListNode start) {ListNode pre = null ;ListNode cur = start;while (cur!=null ){ListNode next = cur.next;return pre;
数组中的第K个最大元素 给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
优化快速排序和堆排序
快速代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public static int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) {int res = sort(nums,0 ,nums.length-1 ,nums.length-k);return res;public static int sort (int nums[],int l,int r,int k) {if (l<=r){int index = quickSort(nums,l,r);if (index==k) return nums[k];else return index<k ? sort(nums,index+1 ,r,k):sort(nums,l,index-1 ,k);return 0 ;public static int quickSort (int nums[],int l,int r) {int t = nums[l];while (l<r){while (l<r && nums[r]>=t){if (nums[r]<t){while (l<r && nums[l]<=t){if (nums[l]>t){return l;
堆排序代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public static int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) {int i = HeapSort(nums, k);return i;public static int HeapSort (int nums[],int k) {for (int i = nums.length/2 -1 ;i>=0 ;i--){for (int i = nums.length-1 ;i>=nums.length-k;i--){if (nums[i]<nums[0 ]){int t = nums[i];0 ];0 ] =t;0 ,i);return nums[nums.length-k];public static void sort (int nums[],int i,int n) {int t = nums[i];for (int a = 2 *i+1 ;a<n;a = 2 *a+1 ){if (a+1 <n && nums[a]<nums[a+1 ]){if (nums[i]<nums[a]){else break ;
二叉树锯齿形层序遍历 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
示例 1:
示例 2:
示例 3:
分析: 使用一个数来控制奇偶,根节点为设置为第一层,所以奇数正序,偶数逆序。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution {public static List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();if (root == null ) return res;int count = 1 ;new LinkedList <>();while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();new LinkedList <>();while (size-- > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (count % 2 == 1 ) {else {if (node.left != null ) {if (node.right != null ) {new ArrayList <>(list1));return res;
三数之和 给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:nums = [-1 ,0 ,1 ,2 ,-1 ,-4 ]1 ,-1 ,2 ],[-1 ,0 ,1 ]]0 ] + nums[1 ] + nums[2 ] = (-1 ) + 0 + 1 = 0 。1 ] + nums[2 ] + nums[4 ] = 0 + 1 + (-1 ) = 0 。0 ] + nums[3 ] + nums[4 ] = (-1 ) + 2 + (-1 ) = 0 。1 ,0 ,1 ] 和 [-1 ,-1 ,2 ] 。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:nums =
示例 3:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [0 ,0 ,0 ][[0,0,0]] 0 。
分析:
固定一个数i,改变l和r。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){if (nums[i]>0 ) continue ;if (i-1 >=0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1 ]) continue ;int l = i+1 ;int r = n-1 ;while (l<r){int sum = nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r];if (sum==0 ){while (l+1 <n && nums[l+1 ]==nums[l]) l++;while (r-1 >=0 && nums[r]==nums[r-1 ]) r--;else if (sum<0 ){else {return res;
搜索旋转排序数组 整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
你必须设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] , target = 0 4
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] , target = 3 1
分析: 二分法,首先将数组进行二分,二分之后两边肯定有一个有序有一个无序,在有序的一边进行查找。无序的一边再进行一分为二。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public int search (int [] nums, int target) {int n = nums.length;if (n==0 ) return -1 ;if (n==1 ) return nums[0 ]==target?0 :-1 ;int left = 0 ;int right = n-1 ;while (left<right){int mid = (left+right)/2 ;if (target==nums[mid]) return mid;if (nums[0 ]<=nums[mid]){if (target<nums[mid] && target>=nums[0 ]){1 ;else left = mid + 1 ;else {if (target>nums[mid] && target<=nums[n-1 ]){1 ;else right = mid - 1 ;if (nums[left]==target) return left;return -1 ;
接雨水 给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:height = [0,1,0,2 ,1,0,1,3 ,2,1,2,1 ]6 0,1,0,2 ,1,0,1,3 ,2,1,2,1 ] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
分析: 每个可以接受雨水的位置是,左右两边最大高度的最小值-该位置的高度。
因此我们可以定义两个数组,来存储每个位置 左边的最大高度 和 右边的最大高度
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i-1],height[i]);
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i+1],height[i]);
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int n = height.length;int leftMax[] = new int [n];int rightMax[] = new int [n];0 ] = height[0 ];for (int i = 1 ;i<n;i++){1 ],height[i]);1 ] = height[n-1 ];for (int i = n-2 ;i>=0 ;i--){1 ],height[i]);int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){return res;
分析:使用双指针,来表示左右连边的最大高度。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int n = height.length;int leftMax = 0 ;int rightMax = 0 ;int left = 0 ;int right = n-1 ;int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){if (height[left]<height[right]){else {return res;
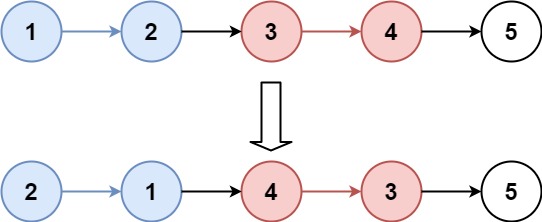
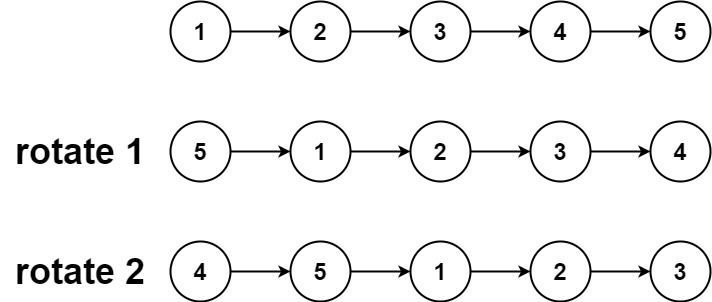
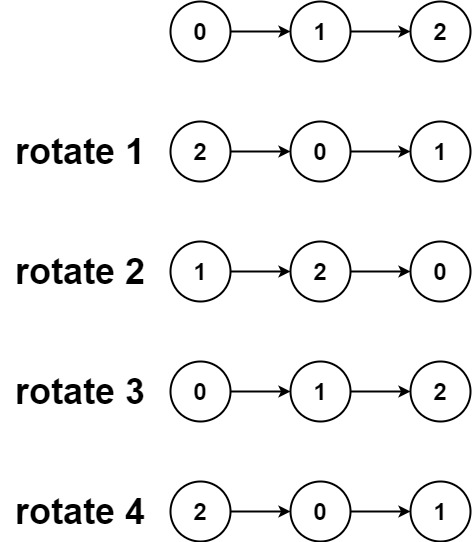
旋转链 表给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] , k = 2 [4,5,1,2,3]
示例 2:
分析:就是将,从尾部开始的第k个节点作为头结点,原来的头结点作为链表结尾的下一个节点。
我们仅需要向右移动 k mod n 次即可。因为每 n 次移动都会让链表变为原状。
我们首先计算出链表的长度 n,
并找到该链表的末尾节点,将其与头节点相连。这样就得到了闭合为环的链表。
然后我们找新链表的最后一个节点,进行断开。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public ListNode rotateRight (ListNode head, int k) {if (head==null || head.next==null ||k==0 ) return head;ListNode p = head;int n = 1 ;while (p.next!=null ){int a = n-k%n;if (a==n){return head;while (a-->0 ){ListNode res = p.next;null ;return res;
买股票的最佳时期 给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4] 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
示例 2:
1 2 3 输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1] 0 0 。
分析:如果我是在历史最低点买的股票就好了!太好了,在题目中,我们只要用一个变量记录一个历史最低价格 minprice,我们就可以假设自己的股票是在那天买的。那么我们在第 i 天卖出股票能得到的利润就是 prices[i] - minprice。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;int max = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i<prices.length;i++){if (prices[i]<minPrice){if (prices[i]-minPrice>max){return max;
合并K个升序链表 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 输入:lists = [[1 ,4 ,5 ],[1 ,3 ,4 ],[2 ,6 ]]1 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,4 ,5 ,6 ]1 ->4 ->5 ,1 ->3 ->4 ,2 ->6 1 ->1 ->2 ->3 ->4 ->4 ->5 ->6
示例 2:
示例 3:
分析:将链表两两合并。像合并两个有序链表一样
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) {ListNode res = null ;for (int i = 0 ;i< lists.length;i++){return res;public ListNode merge (ListNode a,ListNode b) {ListNode pre = new ListNode (0 );ListNode p = pre;ListNode aa = a;ListNode bb = b;while (aa!=null && bb!=null ){if (aa.val<bb.val){else {null ?bb:aa;return pre.next;
螺旋数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private static List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) {new LinkedList <>();if (matrix==null ||matrix.length==0 ) return result;int left = 0 ;int right = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ;int top = 0 ;int bottom = matrix.length - 1 ;int numEle = matrix.length * matrix[0 ].length;while (numEle >= 1 ) {for (int i = left; i <= right && numEle >= 1 ; i++) {for (int i = top; i <= bottom && numEle >= 1 ; i++) {for (int i = right; i >= left && numEle >= 1 ; i--) {for (int i = bottom; i >= top && numEle >= 1 ; i--) {return result;
最有效括号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public int longestValidParentheses (String s) {int maxans = 0 ;new LinkedList <Integer>();1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) {if (s.charAt(i) == '(' ) {else {if (stack.isEmpty()) {else {return maxans;
最长递增子序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 ) {return 0 ;int [] dp = new int [nums.length];0 ] = 1 ;int maxans = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) {1 ;for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {1 );return maxans;
二叉树的最近公共祖先 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {new HashMap <Integer, TreeNode>();new HashSet <Integer>();public void dfs (TreeNode root) {if (root.left != null ) {if (root.right != null ) {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {while (p != null ) {while (q != null ) {if (visited.contains(q.val)) {return q;return null ;
括号生成 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) {new ArrayList <String>();new StringBuilder (), 0 , 0 , n);return ans;public void backtrack (List<String> ans, StringBuilder cur, int open, int close, int max) {if (cur.length() == max * 2 ) {return ;if (open < max) {'(' );1 , close, max);1 );if (close < open) {')' );1 , max);1 );
最短无序连续子数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) {int n = nums.length;int maxn = Integer.MIN_VALUE, right = -1 ;int minn = Integer.MAX_VALUE, left = -1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {if (maxn > nums[i]) {else {if (minn < nums[n - i - 1 ]) {1 ;else {1 ];return right = = -1 ? 0 : right - left + 1 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) {int len = nums.length;int min = nums[len-1 ];int max = nums[0 ];int begin = 0 , end = -1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){if (nums[i] < max){ else {if (nums[len-i-1 ] > min){ 1 ;else {1 ];return end-begin+1 ;