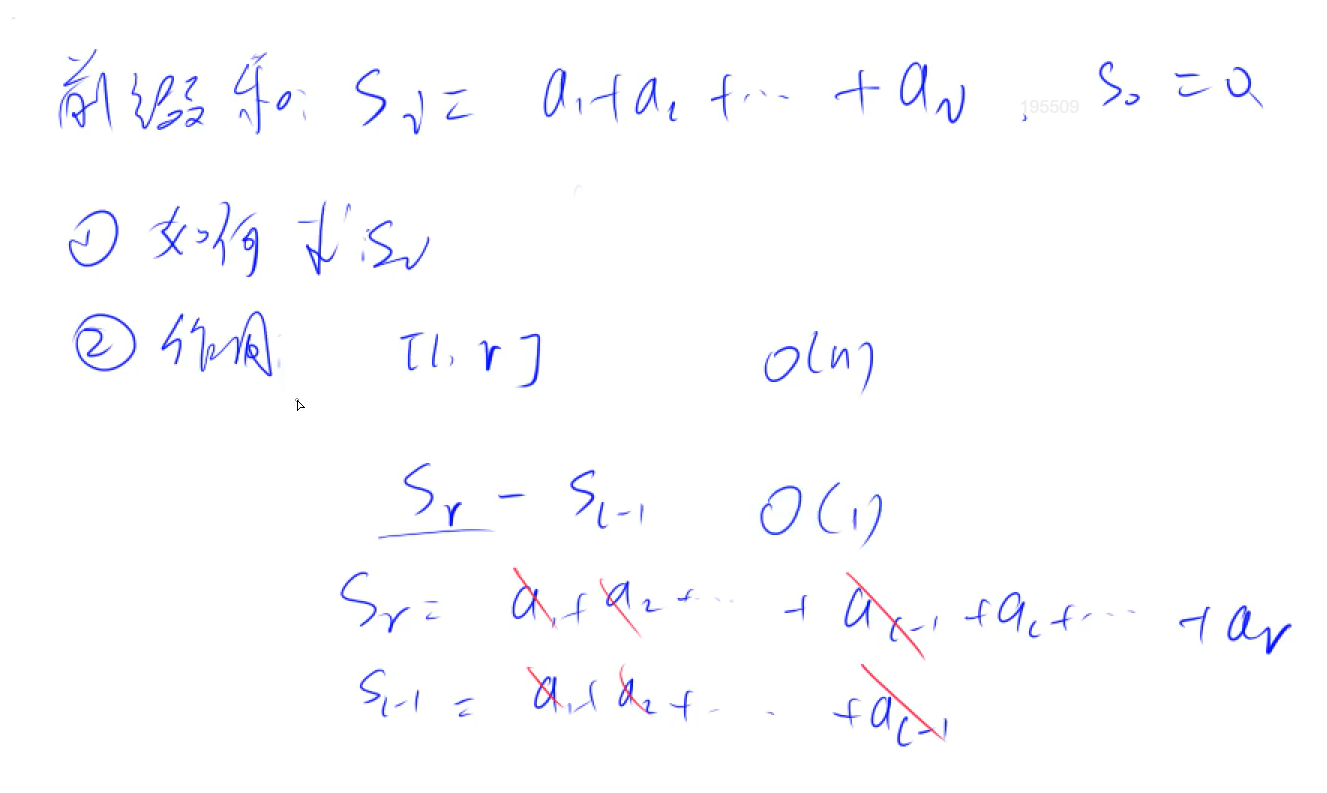前缀和 一维前缀和 计算区间之内的和都可以统一用这个公式:S[r]-S[l-1]
下标必须从1开始,S0 = 0;为了处理边界问题,例如:求[1,10]之间的和:S[10]-S[0],为了所有的区间都可以使用这个公式,所以下标要从1开始,S0设置为0,因为要用到S0.
1 2 S[i] = a[1 ] + a[2 ] + ... a[i]1 ]
例题:
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 m。
第二行包含 n 个整数,表示整数数列。
接下来 m 行,每行包含两个整数 l 和 r,表示一个询问的区间范围。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int M = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];static int s[] = new int [N];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int m = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){1 ] + a[i]; while (m-->0 ){int l = scanner.nextInt();int r = scanner.nextInt();1 ]);
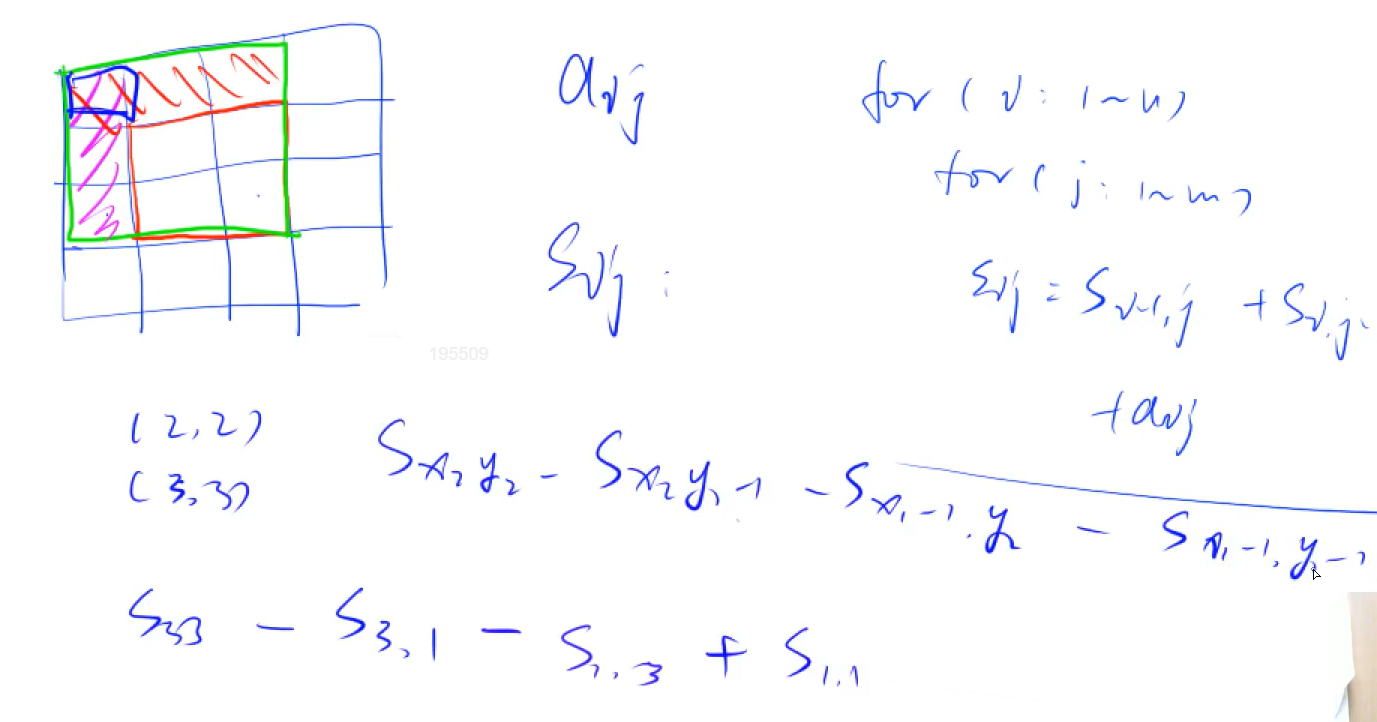
二维前缀和 S[i, j] = 第i行j列格子左上部分所有元素的和 以(x1, y1)为左上角,(x2, y2)为右下角的子矩阵的和为: S[x2, y2] - S[x1 - 1, y2] - S[x2, y1 - 1] + S[x1 - 1, y1 - 1]
推到:
而其中的S[x,y] = S[x-1,y] + S[x,y-1] - S[x-1,y-1] + a[x,y];
例题:
输入格式
第一行包含三个整数 n,m,q。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 m 个整数,表示整数矩阵。
接下来 q 行,每行包含四个整数 x1,y1,x2,y2,表示一组询问。
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import java.io.*;import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 1010 ;static int M = 1010 ;static int Q = 200010 ;static int qq[] = new int [Q];static int s[][] = new int [N][M];static int a[][] = new int [N][M];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int m = scanner.nextInt();int q = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){1 ][j] + s[i][j-1 ] - s[i-1 ][j-1 ]+a[i][j]; while (q-->0 ){int x1 = scanner.nextInt();int y1 = scanner.nextInt();int x2 = scanner.nextInt();int y2 = scanner.nextInt();int res = s[x2][y2] - s[x1-1 ][y2] - s[x2][y1-1 ] + s[x1-1 ][y1-1 ];
差分(前缀和的逆运算) 一维差分 如果给出数组为b , a数组为b数组的前缀和数组,则b数组称为差分数组,。
差分数组一般运用在,给出一个数组,求数组在[l,r]区间内加上某个数之后的数组是多少的问题:
也就是如果要计算这种问题则,则先构造一个差分数组(b[i] = a[i]-a[i-1])。
再将他的差分数组按照以下公式计算即可:
B[l] += c, B[r + 1] -= c
因此,如果要在原数组中改变,。则需要O(n)的时间,但使用差分数组,则只需要改变它的差分数组中的两个数即可,时间复杂度为线性的。
例题:
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];static int b[] = new int [N];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int m = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){1 ];while (m-->0 ){int l = scanner.nextInt();int r = scanner.nextInt();int c = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){1 ] + b[i];for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){" " );public static void insert (int l,int r,int c) { 1 ] = b[r+1 ] - c;
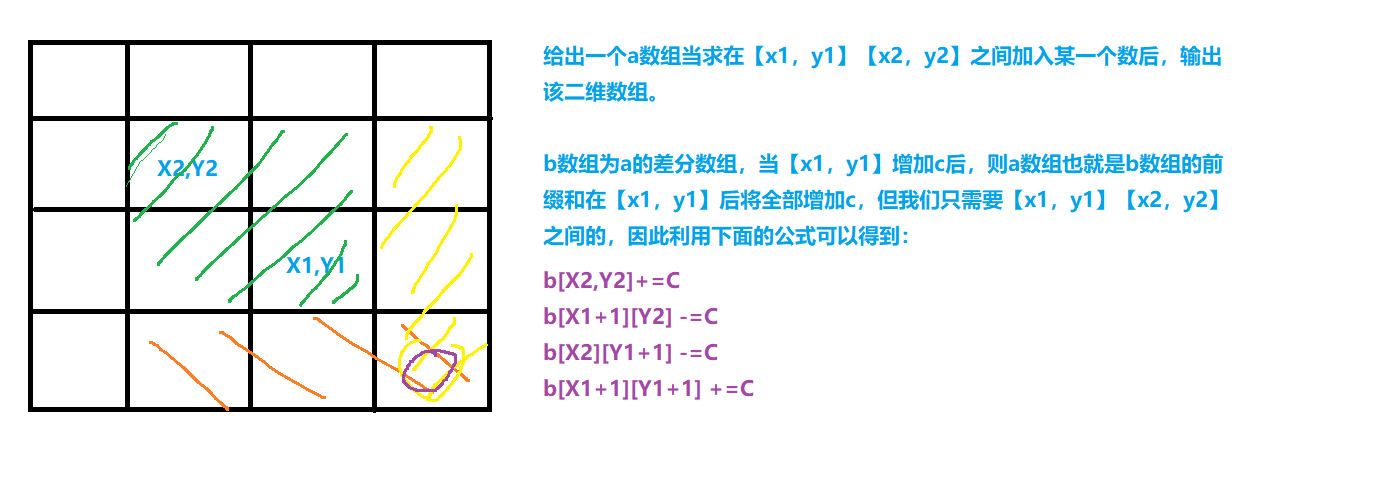
二维差分 S[i, j] = 第i行j列格子左上部分所有元素的和
例题:
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 1010 ;static int M = 1010 ;static int a[][] = new int [N][M];static int b[][] = new int [N][M];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int m = scanner.nextInt();int q = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){while (q-->0 ){int x1 = scanner.nextInt();int y1 = scanner.nextInt();int x2 = scanner.nextInt();int y2 = scanner.nextInt();int c = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){1 ][j] + b[i][j-1 ] - b[i-1 ][j-1 ] + b[i][j];for (int i = 1 ;i<=n;i++){for (int j = 1 ;j<=m;j++){" " );public static void insert (int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int c) {1 ][y1] -=c;1 ] -=c;1 ][y2+1 ] +=c;
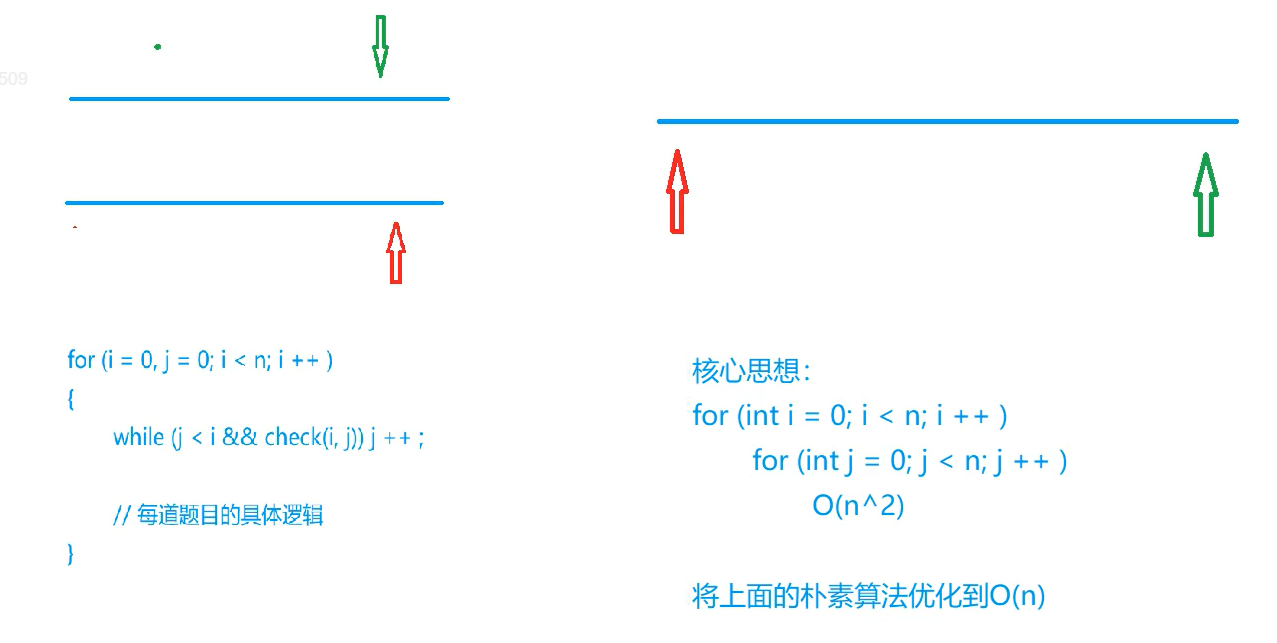
双指针 常见问题分类:
模板:
1 2 3 4 5 6 for (int i = 0 , j = 0 ; i < n; i ++ )while (j < i && check(i, j)) j ++ ;
例题:
代码1为(使用数组):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];static int s[] = new int [N]; public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ,j = 0 ;i<n;i++){while (j<=i && s[a[i]]>1 ) {1 );
代码2为(使用哈希表),当判断的元素不是整数的时候,又可能是字母时,要使用哈希表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];static Map<Object,Integer> map = new HashMap <>();public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){int res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ,j = 0 ;i<n;i++){if (map.containsKey(a[i])) map.put(a[i],map.get(a[i])+1 );else map.put(a[i],1 );while (j<=i && map.get(a[i])>1 ) {1 );1 );
位运算 求n二进制中的第k位数字模板:
n >> k & 1
删除二进制中最后一个1
n&n-1
返回二进制中的最后一个 1
n & -n
例题:
代码1为(使用n&(n-1)):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){int res = 0 ;while (a[i]!=0 ){1 ;" " );
代码2为 (使用n&-n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 static int N = 100010 ;static int a[] = new int [N];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){int res = 0 ;while (a[i]!=0 ){" " );
离散化 针对什么样的问题?
当对于所求数的值域非常大,但在实际的操作过程中,却只用到了一部分的数据,比如求 【l,r】之间的和,只用到了【l,r】之间的数,这时又可能想到利用前缀和的方式,进行计算,但是,值域很大 例如在10的-9次幂,到10的9次幂之间,设置一个数组很显然,不现实
因此,要使用离散化进行数据的映射,将用到的数据,映射到新的链表中,
例题:
代码为l;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 300010 ;static List<Integer> alls = new ArrayList <>();static int a[] = new int [N];static int s[] = new int [N];public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();int m = scanner.nextInt();new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){int x = scanner.nextInt();int c = scanner.nextInt();new Pair (x,c));for (int i = 0 ;i<m;i++){int l = scanner.nextInt();int r = scanner.nextInt();new Pair (l,r));int p = unique();0 ,p);for (Pair pn:pairn){int i = find(pn.first);for (int i = 1 ;i<=alls.size();i++) s[i] = s[i-1 ]+a[i];for (Pair pm:pairm){int l = find(pm.first);int r = find(pm.second);1 ]);public static int find (int x) {int l = 0 ;int r = alls.size()-1 ;while (l<r){int mid = l+r>>1 ;if (alls.get(mid)>=x) r = mid;else l = mid + 1 ;return r+1 ;public static int unique () {int j = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ;i<alls.size();i++){if (i==0 || alls.get(i)!=alls.get(i-1 )){return j;class Pair {int first;int second;public Pair (int first, int second) {this .first = first;this .second = second;
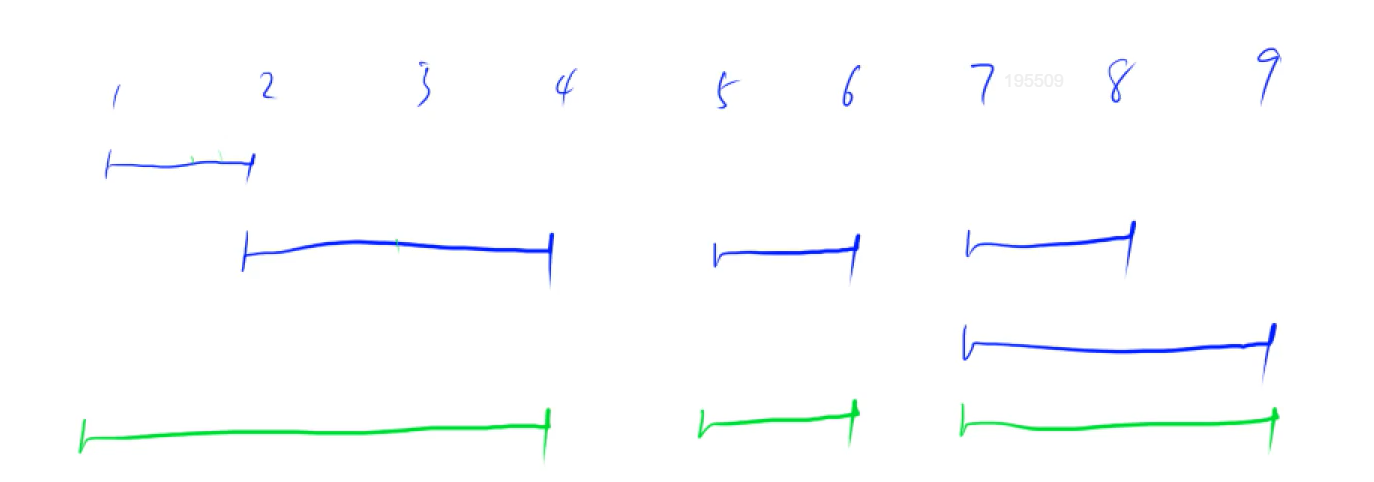
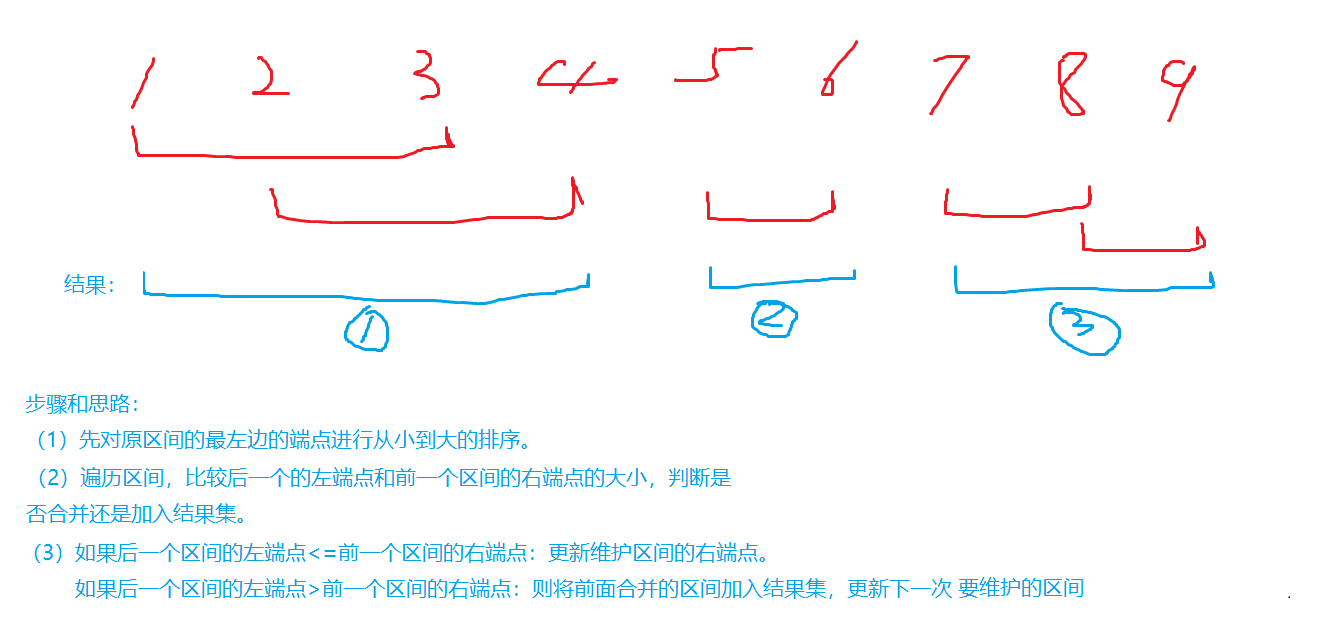
区间合并 题型:
有n个区间,把所有 有交集的区间进行合并,最后求出合并后区间的个数
多个区间,如果有交集的就进行合并。如下图所示:最后合并完的区间为3个
思想和步骤:
代码模板:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int l = (int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ));int r = (int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ));for (int k[]:list){if (k[0 ]>r){if (l!=(int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ))) res.add(new int []{l,r});0 ];1 ];1 ]);if (l!=(int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ))) res.add(new int []{l,r});
例题:
代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import java.util.*;public class Main {static int N = 100010 ;static int a[];static List<int []> list = new ArrayList <>();static List<int []> res = new ArrayList <>();public static void main (String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);int n = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++){new int [2 ];int l = scanner.nextInt();int r = scanner.nextInt();0 ] = l;1 ] = r;new Comparator <int []>() {@Override public int compare (int [] o1, int [] o2) {return o1[0 ]-o2[0 ];int l = (int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ));int r = (int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ));for (int k[]:list){if (k[0 ]>r){if (l!=(int )(-2 *Math.pow(10 ,9 ))) res.add(new int []{l,r});0 ];1 ];1 ]);new int []{l,r});